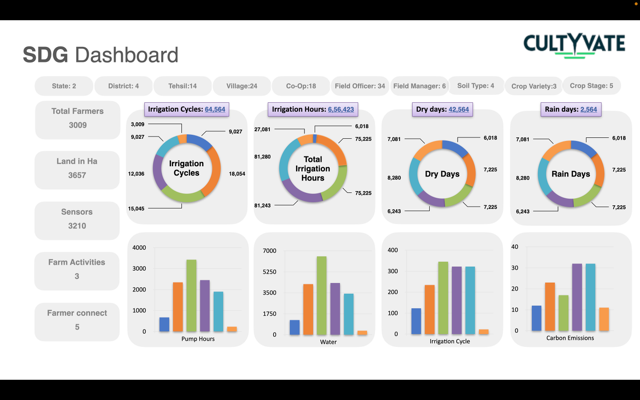
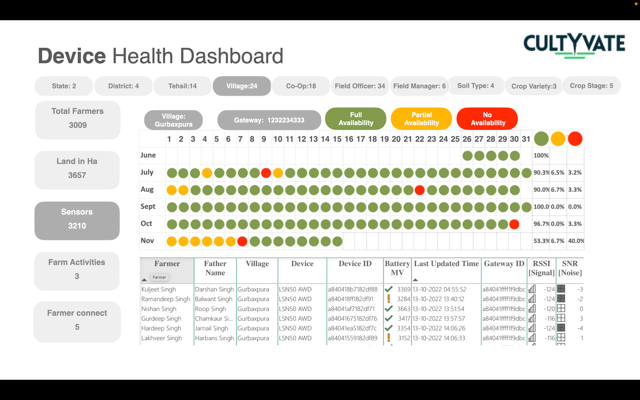
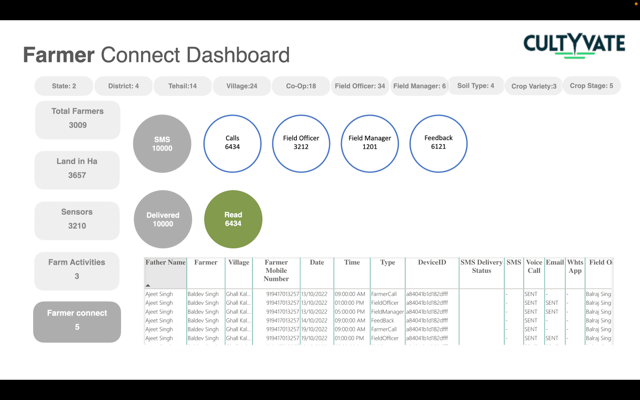
SDG Impact

SDG1 – Generate stable income through sustainable rice production.

SDG2 – Support farming communities in producing climate, smart rice cultivation and sustainable irrigation methods, And enhancing knowledge about agricultural production.

SDG6 – through sustainable water management practices in rice cultivation, water is efficiently used. Resulting in stable water supply.

SDG12 – ensure sustainable productions and production patterns.

SDG13 – fight climate change by avoiding CH4 emissions from continuously flooded patties.